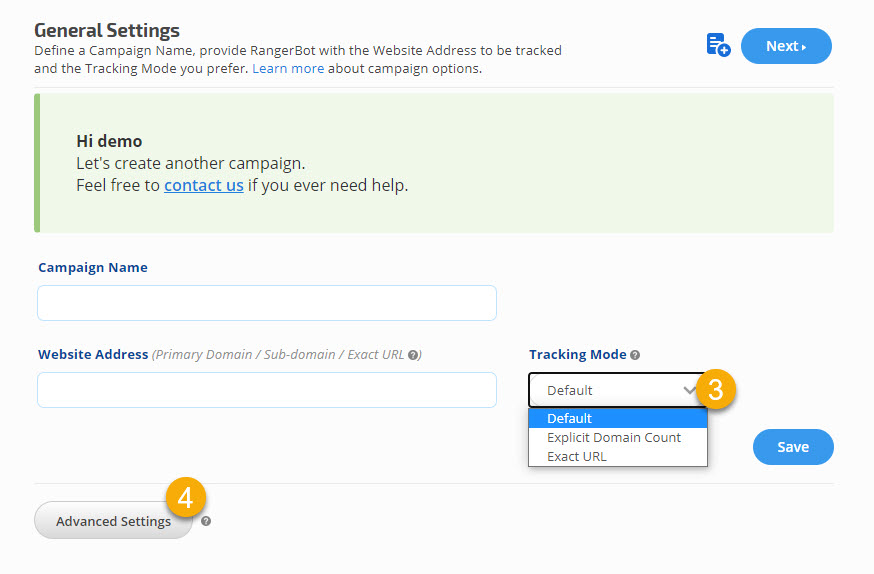
Rank Ranger allows you to customize our rank tracking software by selecting aspects of how it counts the rankings that it collects for you; providing you with multiple options to choose from. You can choose to monitor Default (count exactly as displayed in SERPs), Explicit Domain Count, or Exact URL ranking.
- SEO
- Rank Tracker
- Local SEO
- Mobile SEO
- Link Manager
- Landing Pages
- Social Signals
- On-Page Optimization
- Enterprise SEO Solutions
- Marketing
- Competition Analysis
- Insight Graph
- Keyword Research
- Graphs & Widgets
- Market Reach
- Marketing KPI
- Brand Visibility
- White Label SEO
- Marketing Dashboard
- Client Dashboard
- PDF Reports
- PDF Templates
- Other
- Email Notifications
- Portfolio Management
- Integrations
- Google Analytics
- Search Console
- Pay Per Click
- WeDevelop
- API
Documentation
> Campaigns >
Rank Tracker Settings
Tracking Mode
Anatomy of SERPs
Understanding Search Engine Results Page Terminology
Before explaining the rank tracking modes, let's examine some SERP terminology to gain a better understanding of what users experience when searching for keywords and how our rank tracker reports search results.

Figure 1. Search Engine Results Page terminologyBefore explaining the rank tracking modes, let's examine some SERP terminology to gain a better understanding of what users experience when searching for keywords and how our rank tracker reports search results.

Default Tracking Mode (Domain and Sub-domains)
The Default Tracking Mode is used to count rank results for domains and sub-domains as is when tracking rankings in search engine results.
Select Default Tracking Mode when you want to monitor domains (e.g. yoursite.com/*), or sub-domains (e.g., *.yoursite.com/*).
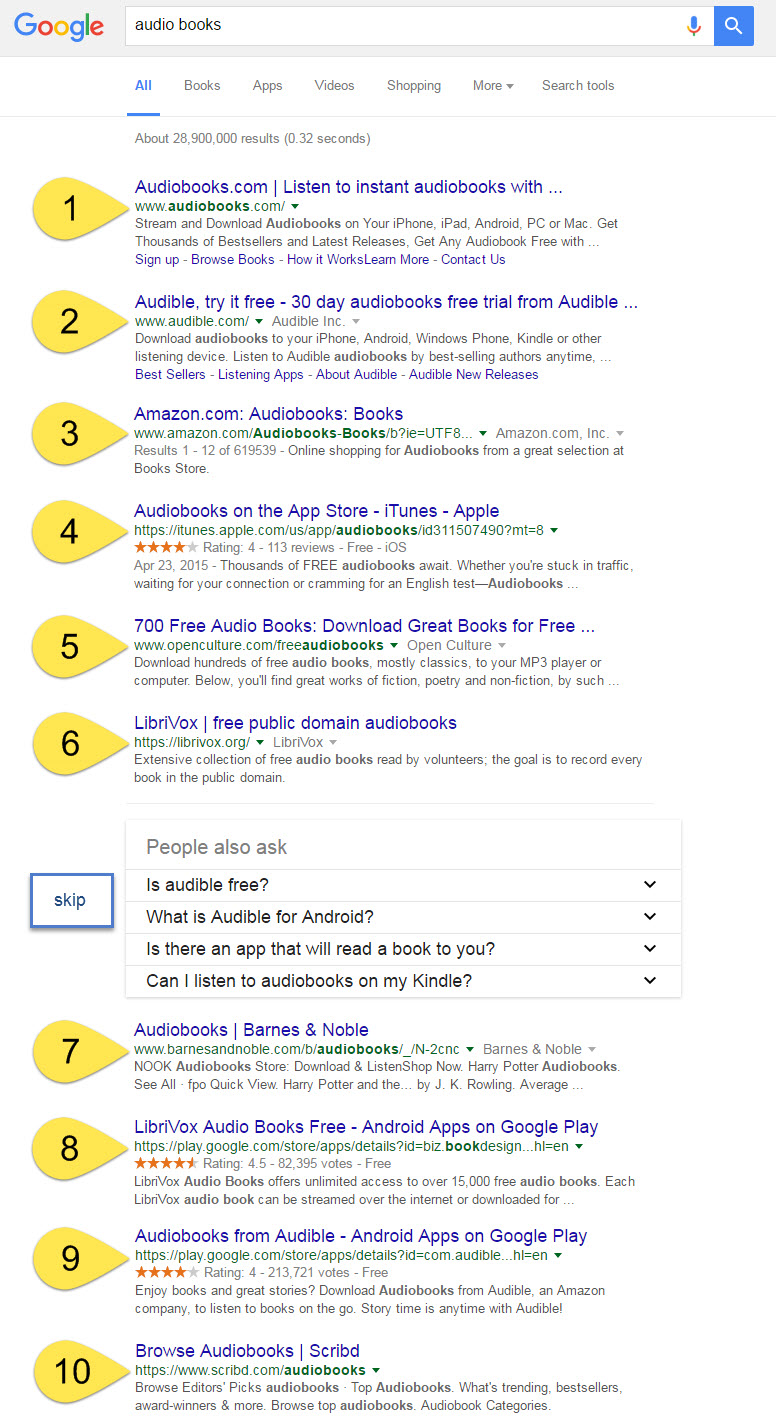
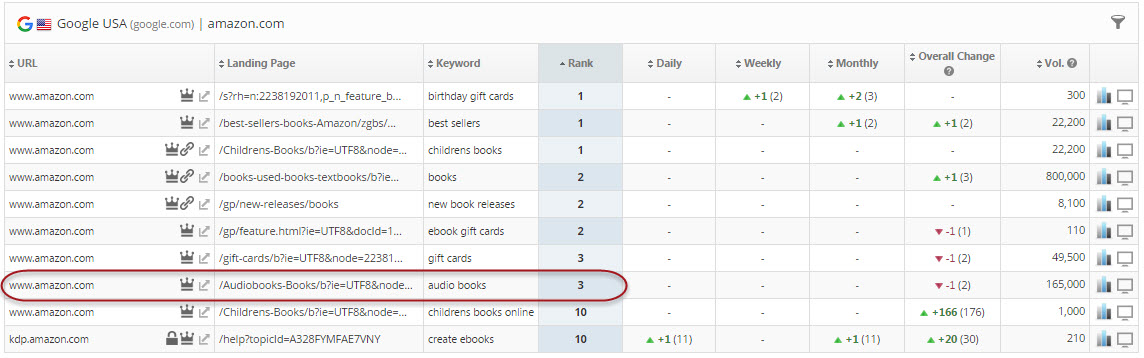
Figure 3. Rank tracking report provides a sampling of Amazon's keyword rank results on Google USA.
Learn more about Organic Indicators in search results.
Select Default Tracking Mode when you want to monitor domains (e.g. yoursite.com/*), or sub-domains (e.g., *.yoursite.com/*).
Figure 3. Rank tracking report provides a sampling of Amazon's keyword rank results on Google USA.
Learn more about Organic Indicators in search results.
Explicit Domain Count
Explicit Domain Count ignores duplicates of a domain in search engine results.
Use Explicit Domain Count Tracking Mode when you want to monitor domains (e.g. yoursite.com/*), or sub-domains (e.g., *.yoursite.com/*).
Use Explicit Domain Count Tracking Mode when you want to monitor domains (e.g. yoursite.com/*), or sub-domains (e.g., *.yoursite.com/*).
The red numbers demonstrate Google's organic results rank, while the yellow numbers depict how Rank Ranger counts the rankings when Explicit Domain Count is the selected Tracking Mode.
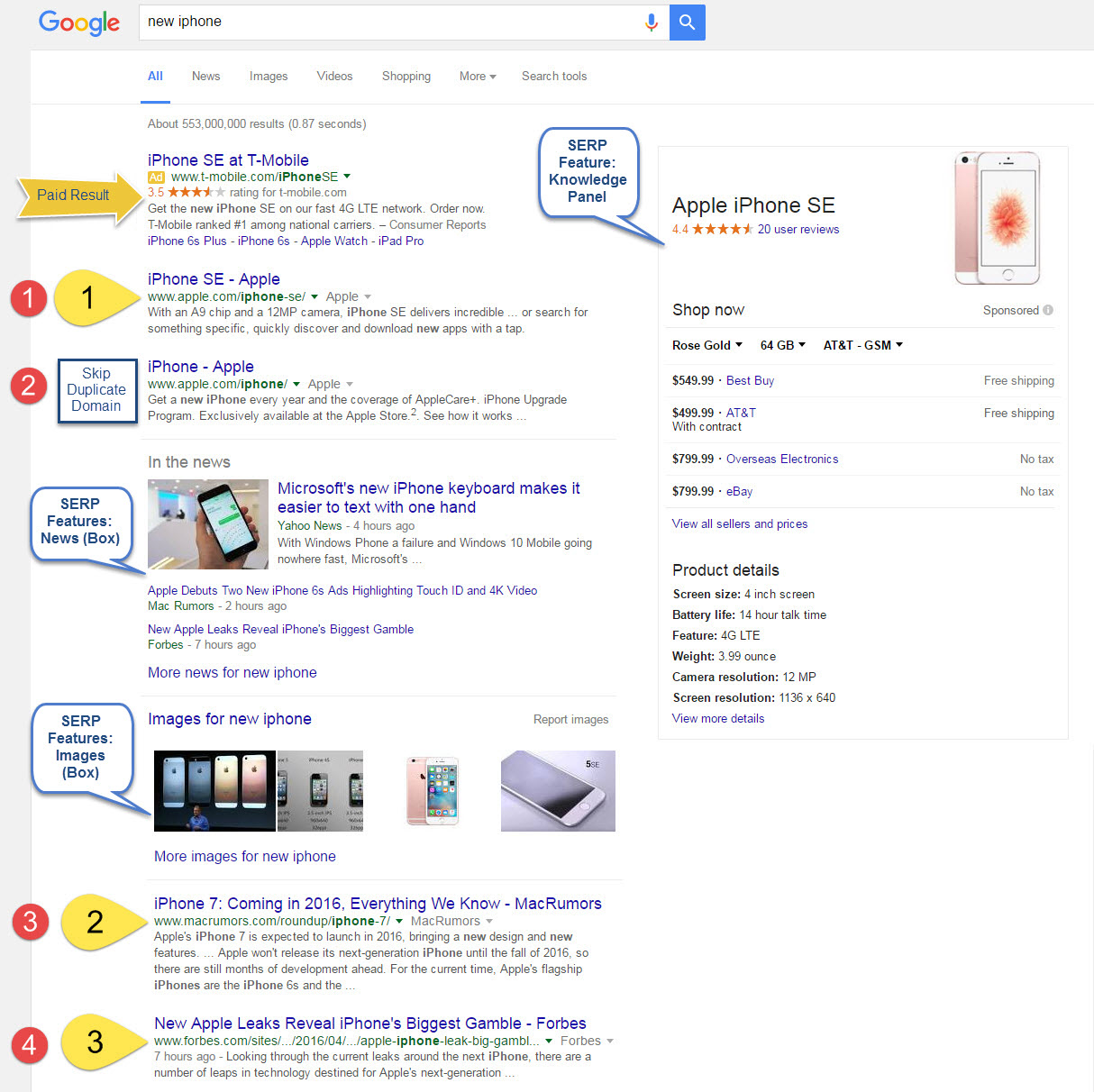

Figure 4. Explicit Domain Count Rank Tracking Mode is represented by the yellow numbers.
Learn more about including News results in the rank count, and Google SERP Features.
Rank Tracking Dashboard
A view of the above results for Apple's "new iPhone" keyword in the Rank Tracker Dashboard.
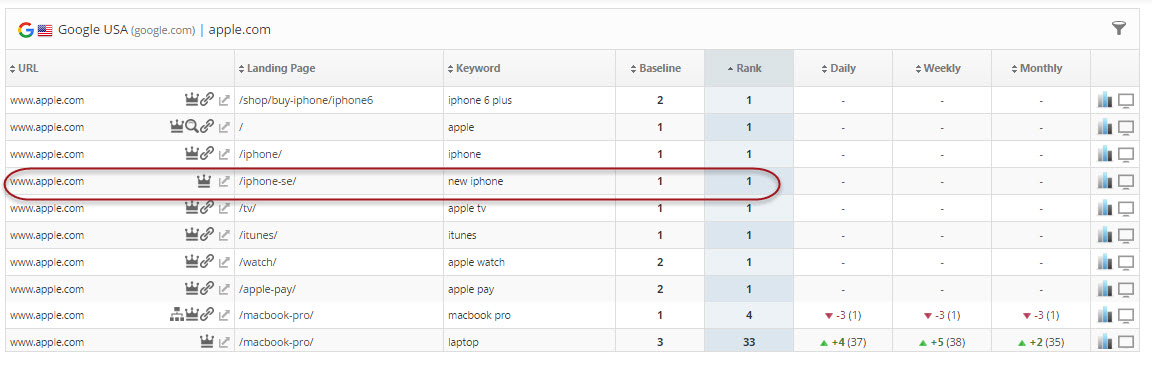
Figure 5. A sampling of Apple's keyword rankings in our Rank Tracker Dashboard report.Learn more about including News results in the rank count, and Google SERP Features.
Rank Tracking Dashboard
A view of the above results for Apple's "new iPhone" keyword in the Rank Tracker Dashboard.

Exact URL (Track Sub-Directory or Specific Page)
Exact URL rank tracking mode tracks and counts the rank of a specific page or section within a website. When you choose this option Rank Ranger will match the results only if the exact URL matches the search engine result.
Use when you want to track a sub-directory (e.g. http://site.com/subdirectory/) or specific landing page (e.g., http://site.com/yourpage.html), this is also one of the options to choose for tracking keywords in YouTube, Apple iTunes, and Google Play Stores (the other option is tracking in Default mode and adding Target URLs to keywords in Campaign Settings).
Please note that you will only be able to insert a specific URL for your campaign if you have selected this option. If you select one of the alternative rank tracking mode options, then any sub-directory and/or landing page entered will be stripped and only the domain name (e.g., yoursite.com) will be used for rank tracking.
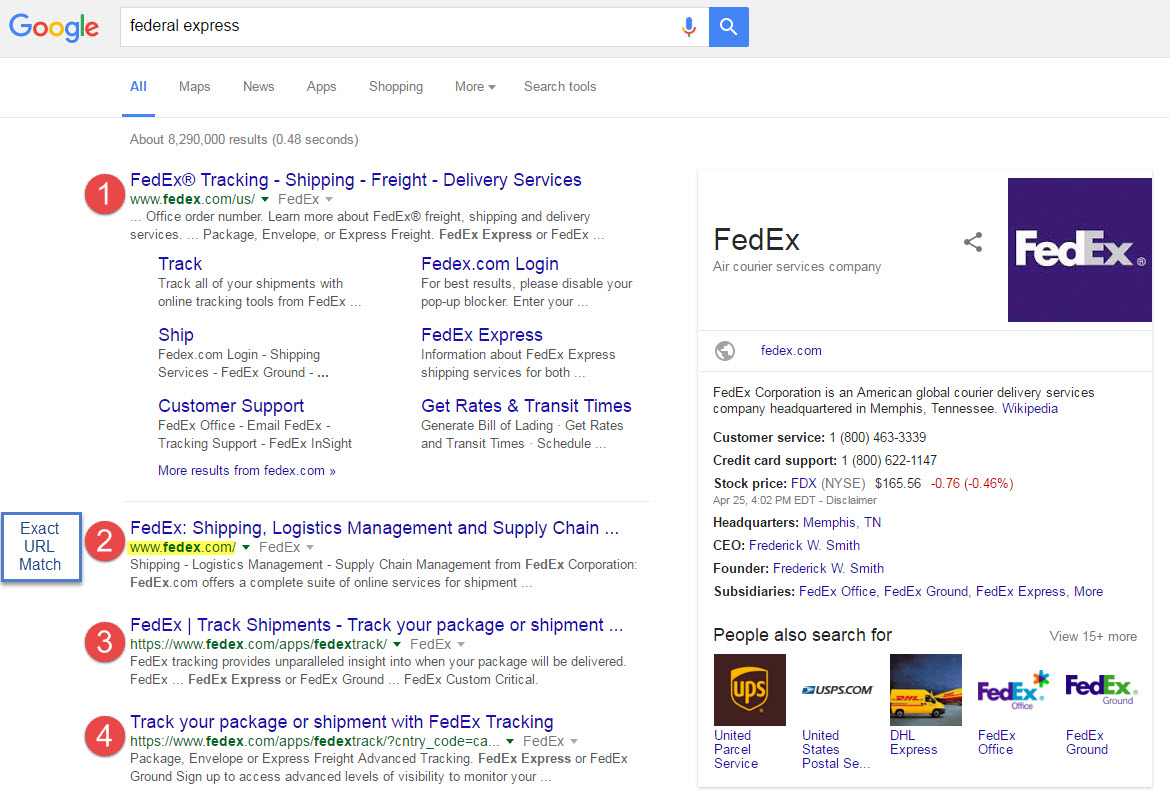
Figure 6. SERP ranking for the search phrase "federal express".
If a sub-directory such as https://www.fedex.com/us/ had been entered, then the first result displayed in the SERP example above would have been counted as the rank for the keyword.
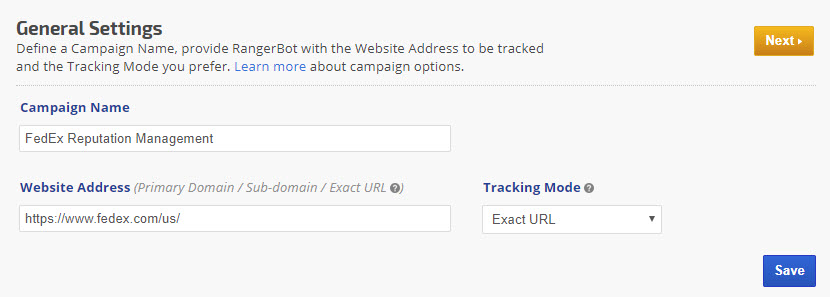 Figure 7.1. Campaign Settings displaying Exact URL tracking for a sub-directory.
Figure 7.1. Campaign Settings displaying Exact URL tracking for a sub-directory.
Figure 9. YouTube search results for the keyword "Lego"
Figure 10. Rank Tracker Dashboard displays the primary Lego Shopping video rank, along with other Exact URLs being tracked in this YouTube rank tracking campaign.
Note: to rank track a YouTube Channel in a YouTube search, we recommend selecting the Default Tracking Mode and using Target URLs with a wildcard (refer to Add Target URL documentation).
Use when you want to track a sub-directory (e.g. http://site.com/subdirectory/) or specific landing page (e.g., http://site.com/yourpage.html), this is also one of the options to choose for tracking keywords in YouTube, Apple iTunes, and Google Play Stores (the other option is tracking in Default mode and adding Target URLs to keywords in Campaign Settings).
Please note that you will only be able to insert a specific URL for your campaign if you have selected this option. If you select one of the alternative rank tracking mode options, then any sub-directory and/or landing page entered will be stripped and only the domain name (e.g., yoursite.com) will be used for rank tracking.
Figure 6. SERP ranking for the search phrase "federal express".
In this reputation management campaign example, the home page of fedex.com was entered as the tracked website address, along with the Exact URL tracking mode. Because there is no sub-directory or specific landing page in the Website Address field, RangerBot will only match the exact URL as listed: www.fedex.com when reporting the rank position for this campaign's keywords. The goal of this campaign is to track the additional website URLs entered because they are related to the site's online reputation.
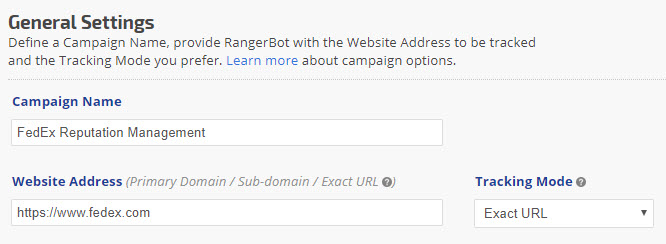
Figure 7. Campaign Settings displaying the Exact URL Tracking Mode.
If a sub-directory such as https://www.fedex.com/us/ had been entered, then the first result displayed in the SERP example above would have been counted as the rank for the keyword.

Rank Tracker Dashboard
In this example, the keyword "federal express" is ranked as being in the number 2 position in Google USA search results due to the Exact URL setting for only the site's home page.
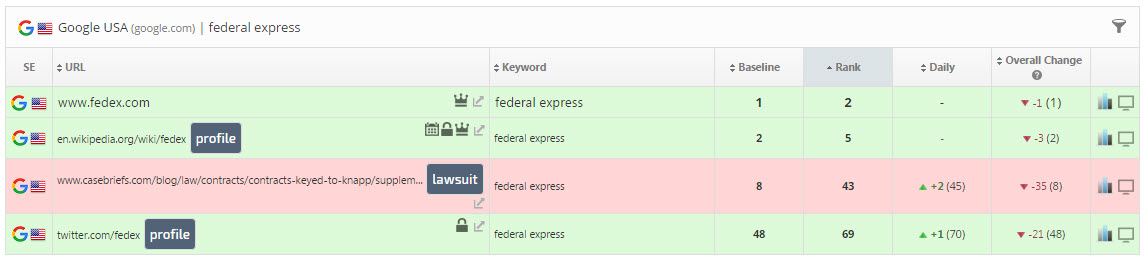
Figure 8. Rank Tracker Dashboard for a reputation management campaign displays the positive and negative impact of specific URLs ranking for the site's keywords.In this example, the keyword "federal express" is ranked as being in the number 2 position in Google USA search results due to the Exact URL setting for only the site's home page.

Exact URL Tracking of YouTube Videos
The yellow numbers represent how Rank Ranger counts YouTube search results for the Exact URL being tracked in a Lego campaign.
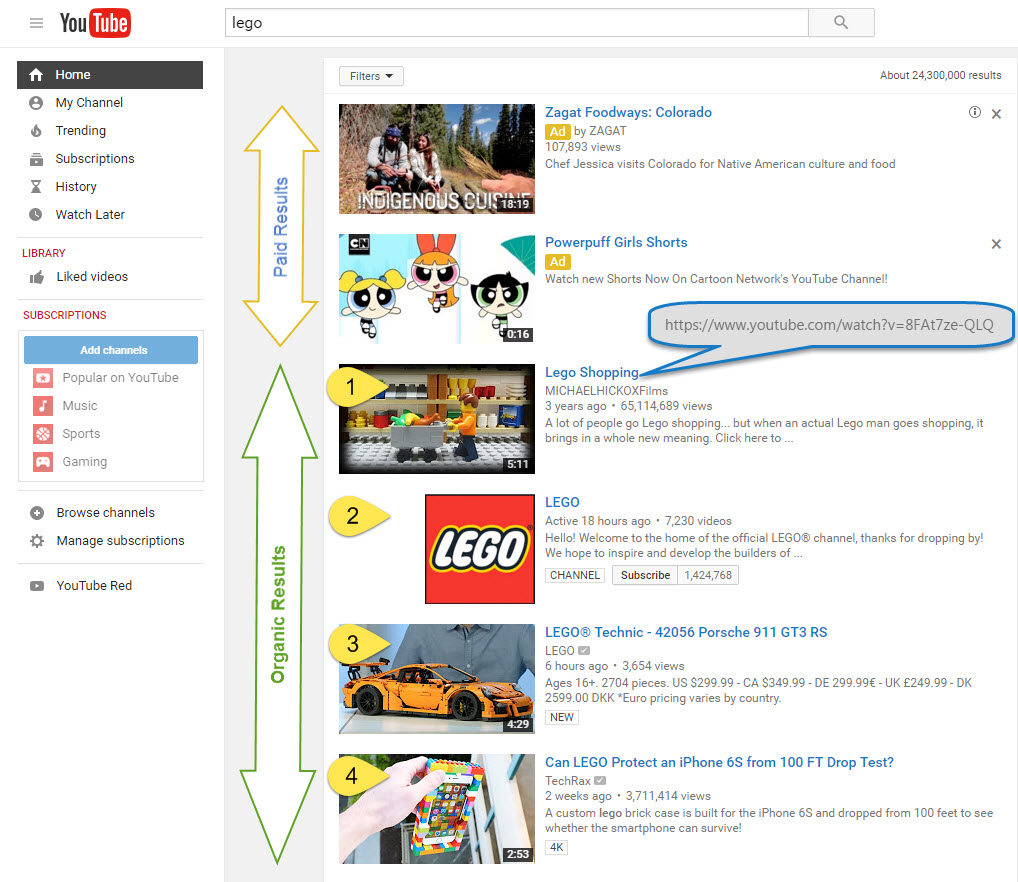
The yellow numbers represent how Rank Ranger counts YouTube search results for the Exact URL being tracked in a Lego campaign.

Figure 9. YouTube search results for the keyword "Lego"
Rank Tracker Dashboard Tracking Exact URLs in YouTube
In this example, the keyword "Lego" is ranked for the YouTube Exact URL (tagged as Lego Shopping) in position 1.
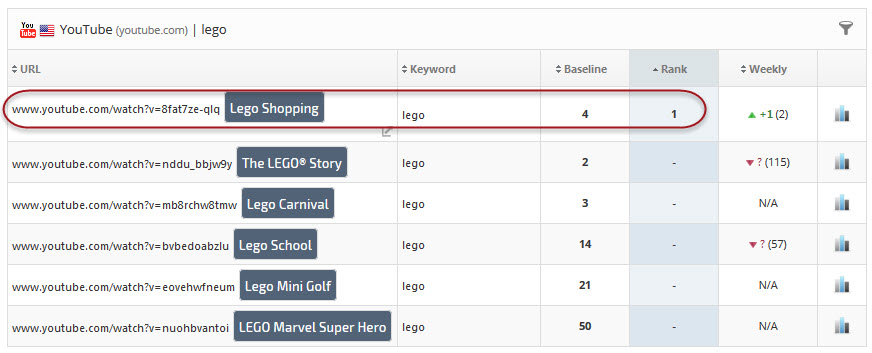
In this example, the keyword "Lego" is ranked for the YouTube Exact URL (tagged as Lego Shopping) in position 1.

Figure 10. Rank Tracker Dashboard displays the primary Lego Shopping video rank, along with other Exact URLs being tracked in this YouTube rank tracking campaign.
Note: to rank track a YouTube Channel in a YouTube search, we recommend selecting the Default Tracking Mode and using Target URLs with a wildcard (refer to Add Target URL documentation).
Exact URL Rank Tracking for Google Play Store Apps
The yellow numbers represent how Rank Ranger counts the rankings for the Exact URLs entered in the primary domain and competitor websites Campaign Settings screen.

The yellow numbers represent how Rank Ranger counts the rankings for the Exact URLs entered in the primary domain and competitor websites Campaign Settings screen.

Figure 11. Google Play Store search results for the keyword "video chat".
Google Play Store Rank Tracker Dashboard
A view of the above results in the Dashboard for the video chat campaign.
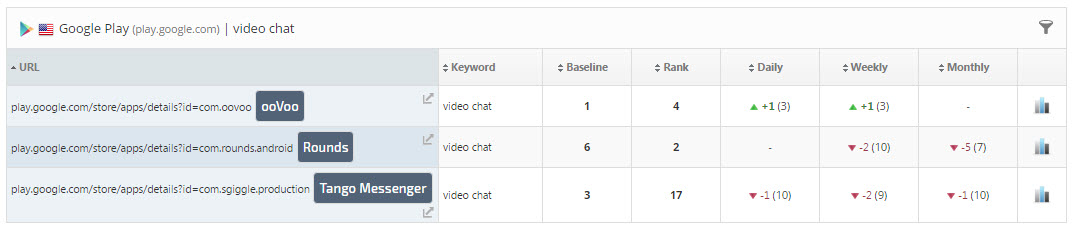
Figure 12. Google Play Store rankings for the keyword "video chat" for the primary App as well as competitor's App rankings. Google Play Store Rank Tracker Dashboard
A view of the above results in the Dashboard for the video chat campaign.

Root Domain vs. Sub-directory and Sub-domain Terminology
To explain these terms, we should start with an example URL: http://www.example.com/cameras/?q=digital&id=2
A URL is made up of the following parts: a protocol (http://), domain (www.example.com), subdirectory (/cameras), query strings (?q=digital) and resource id (id=2).
Root Domain
The root domain of a site is the highest level within the Internet domain structure. The root domain name itself does not have a specific name, and it contains the top-level domain - or domain extensions - such as .com, .org, or .net. The Root domain also contains the second-level domain, or that part of the domain which is typically readable, such as "rankranger" on www.rankranger.com. A third-level domain refers to the domain host, and precedes the two other parts of the root domain. "www" is the most common third-level domain, but some domains may include additional servers, listed as "WWW2” etc. Many people using the "root domain" term refer to the entire contents of the same domain, even if that is not entirely accurate. The correct term for the sum of the parts of the domain is the Internet domain name.
Sub-domain
The Sub-domain is a component of a lower level of a domain, often in a separate part of the site. A marketing reports site section might be defined as reports.companyname.com this allows it to be sectioned off for secure login access for customers to view reports (refer to our White Label Custom Domain service for a use example). The separation of part of a site into its sub-domain also makes it more convenient to track users who visit the site for a specific type of content. Sub-domains also enable webmasters to create a more specialized site without buying a new domain - for example, the main business site as well as sub-domains for each individual country or language (e.g, us.companyname.com).
Sub-directories
It can be easy to confuse sub-domains with sub-directories. The sub-directory is a file folder within the site's architecture, using a specific format like: www.companyname.com/en-us. Sub-directories, enable the creation of categories of content for better content organization. In the example, the company is using a ‘en-us’ folder to hold files for the English site which is focused on the United States.
A URL is made up of the following parts: a protocol (http://), domain (www.example.com), subdirectory (/cameras), query strings (?q=digital) and resource id (id=2).
Root Domain
The root domain of a site is the highest level within the Internet domain structure. The root domain name itself does not have a specific name, and it contains the top-level domain - or domain extensions - such as .com, .org, or .net. The Root domain also contains the second-level domain, or that part of the domain which is typically readable, such as "rankranger" on www.rankranger.com. A third-level domain refers to the domain host, and precedes the two other parts of the root domain. "www" is the most common third-level domain, but some domains may include additional servers, listed as "WWW2” etc. Many people using the "root domain" term refer to the entire contents of the same domain, even if that is not entirely accurate. The correct term for the sum of the parts of the domain is the Internet domain name.
Sub-domain
The Sub-domain is a component of a lower level of a domain, often in a separate part of the site. A marketing reports site section might be defined as reports.companyname.com this allows it to be sectioned off for secure login access for customers to view reports (refer to our White Label Custom Domain service for a use example). The separation of part of a site into its sub-domain also makes it more convenient to track users who visit the site for a specific type of content. Sub-domains also enable webmasters to create a more specialized site without buying a new domain - for example, the main business site as well as sub-domains for each individual country or language (e.g, us.companyname.com).
Sub-directories
It can be easy to confuse sub-domains with sub-directories. The sub-directory is a file folder within the site's architecture, using a specific format like: www.companyname.com/en-us. Sub-directories, enable the creation of categories of content for better content organization. In the example, the company is using a ‘en-us’ folder to hold files for the English site which is focused on the United States.
Select a Ranking System
To customize your Rank Ranger rankings, follow the instructions for the Campaign Settings > General screen options.